CMYK v/s RGB: Which Works Best For Web To Print Business
When it comes to web-to-print businesses, color is indeed the most powerful tool. From grabbing attention to influencing purchasing decisions, and building brands, it provides businesses with a lot of benefits. But the real problem arises while selecting the color mode for designing. Whether it should be CMYK or RGB? A dilemma often people face!
Through this article, we aim to address this dilemma as we are going to explore these two dominant color modes and their impact on web-to-print workflows. So without any further delay, let’s begin.
Understanding CMYK and RGB
CMYK
CMYK stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key Black. These four inks are the building blocks for printed colors. You can imagine these inks as tiny dots layering on top of each other to form the final image.
Coming to the process, so CMYK operates on a subtractive color mixing process, meaning white light reflects off the paper, and inks absorb specific wavelengths of light. Therefore, as more ink is layered (combined), more light is absorbed, resulting in darker or more muted colors.
For example, if you combine cyan and magenta inks, it will subtract red and green light, creating blue.
RGB
RGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue. These are the primary colors of light that combine to form the vast spectrum of colors we see on digital screens. In simple words, each pixel you see on your monitor is composed of tiny subpixels that emit red, green, and blue light at varying intensities.
Coming to the process, RGB utilizes an additive color mixing process which means the more colors you combine, the brighter and more saturated the resulting light becomes. In RGB, black is the absence of light, while increasing the intensity of all three colors (red, green, and blue) creates white light.
Difference Between CMYK and RGB
The primary difference between CMYK and RGB lies in their color gamut meaning the range of colors they can produce.
RGB, on one side, boasts a wider gamut which means it can represent a broader range of vibrant and saturated colors, ideal for the rich visuals we see on screens. You can think of those neon greens and blues that usually grab your attention on a website.
On the other side, CMYK has a more limited gamut. Here, inks can only absorb, not emit light, which results in a smaller range of colors that appear slightly more muted compared to that of RGB. The reason for so is that, here the perfect black is difficult to achieve by mixing CMY inks, so a dedicated black ink (K) is used.
CMYK for Print: Advantages and Considerations
Advantages
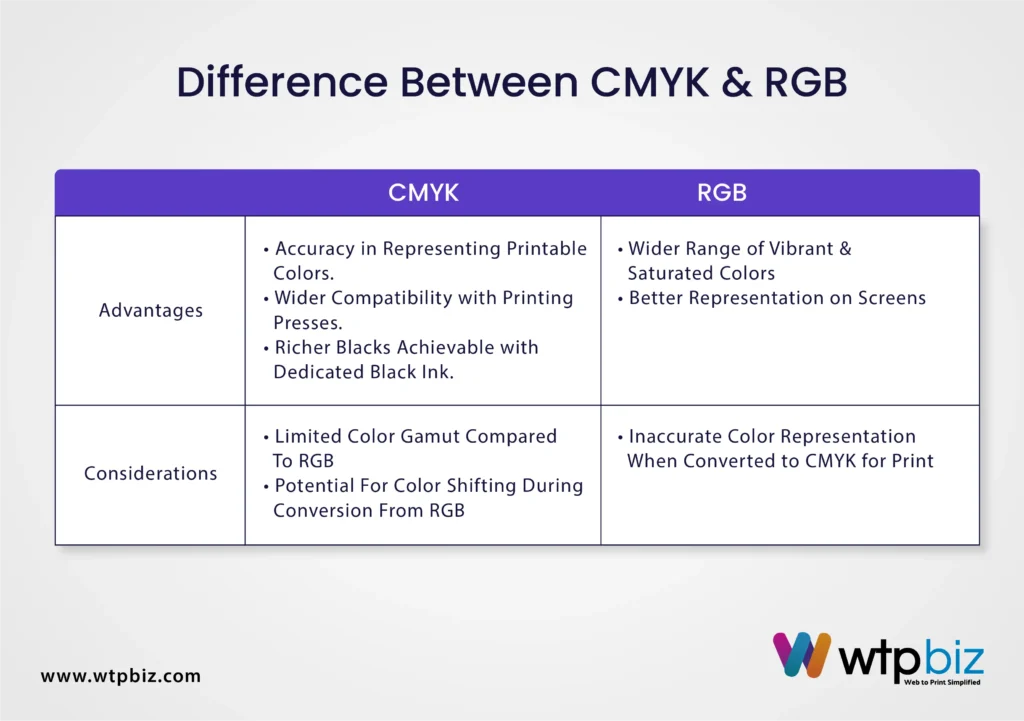
- Accuracy in Representing Printable Colors: CMYK inks directly correspond to the printing process which ensures the colors you design with are accurately translated onto paper. This eliminates the guesswork and potential for color surprises during the emergence of the final product from the press.
- Wider Compatibility with Printing Presses: Since the vast majority of printing presses rely on the CMYK ink system your design files can readily be understood and processed by printers without the need for complex color conversions.
- Richer Blacks Achievable with Dedicated Black Ink: When you mix cyan, magenta, and yellow inks it can result in a dull or muddy black, which can be a problem in certain cases. With CMYK this problem gets addressed as it includes a separate black ink (Key Black) which provides deep and rich blacks, thus enhancing the overall visual impact of your printed materials.
Considerations
- Limited Color Gamut Compared to RGB: As already mentioned, the CMYK color spectrum is inherently smaller than that of RGB. The vibrant and highly saturated colors achievable on screens might not translate perfectly to print since inks here can only absorb and not emit light, thus resulting in a slightly muted color range.
- Potential for Color Shifting During Conversion from RGB: If you design primarily in RGB and then convert to CMYK for printing, there’s a chance some colors might shift slightly as certain RGB colors fall outside the printable CMYK gamut.
RGB for Digital: Advantages and Considerations
Advantages
- Wider Range of Vibrant and Saturated Colors: As already mentioned, RGB boasts a broader color gamut compared to that of CMYK which means a wider array of stunningly vivid and saturated colors can truly pop on your digital screens. This makes RGB ideal for grabbing attention and creating a visually captivating experience for website visitors or app users.
- Better Representation on Screens (Monitors, Mobile Devices): Since RGB aligns with how pixels on digital displays generate color, it ensures a more accurate representation of your design intent. The colors will appear exactly as intended on the screens thus giving your audiences a richer experience.
Considerations
- Inaccurate Color Representation When Converted to CMYK for Print: Getting the beauty of RGB on screens can be a challenging task if you decide to translate it to print. This is so because some of the RGB colors might not be faithfully reproduced by CMYK inks, which will lead to color shifting and a less vibrant final product.
Best Practices While Working with CMYK and RGB in a Web-to-Print Business
Now that we have understood the strengths and limitations of both CMYK and RGB, let’s discuss the best practices while working with them in a web to print businesses.
- Design Primarily in RGB for On-Screen Visuals: If you want to create eye-catching visuals for your website, app, or other digital interfaces, try to leverage the wider gamut of RGB as this will ensure a vibrant and engaging user experience.
- Maintain Editable RGB Files for Future Modifications: Always keep editable versions of your designs in RGB format as this will allow the team to make easy adjustments if needed and future design iterations as well.
- Convert to CMYK Only Before Finalizing Print Files: When converting to CMYK mode, ensure your design is finalized for print as this will ensure the colors are translated as accurately as possible within the limitations of the printing process.
- Communicate Color Expectations with Clients and Printers: Discussing color expectations with both clients and printers is very important, so don’t miss out on this. Share the CMYK color profiles or swatches so as to ensure everyone is on the same page regarding the final printed colors.
- Consider Using Spot Colors (PMS) for Consistent Brand Colors: For brand colors that require precise replication across both digital and print materials, consider using spot colors that are defined by the Pantone Matching System (PMS). These colors use pre-mixed inks which offers more consistent color results compared to that of CMYK.
Common Challenges and Solutions for Web-to-Print Color Consistency
Color Shifting During Conversion
While converting designs from RGB to CMYK, there can be slight color variations in the result. This can be avoided by calibrating the monitor at regular intervals so as to ensure accurate color representation.
Limited CMYK Gamut
Since certain vibrant RGB colors might not have a perfect match in the CMYK spectrum, you can consider using a more limited color palette for your designs that translate well to print.
Printer Variations
Another thing that can affect the final printed colors is printing presses and papers, therefore always work with a reputable printer who can provide consistent results.
How WTPBiz can be helpful here?
At WTPBiz, we are a team of skilled professionals dedicated to tackling any challenge in the print industry. We are a web-to-print agency, that develops fully functional and secure w2p solutions to attract more buyers and streamline online sales through automation. Our solutions are customized to meet the needs of both B2B and B2C clients, using the latest technologies. In addition to providing online design solutions, we also act as technology partners for our clients.
Conclusion
This world of color is a complex landscape, especially if you are a business that is looking to navigate both web and print. To make informed decisions, all you have to do is understand the distinct roles of CMYK and RGB. this will help you in making informed decisions.
Remember, CMYK is good for print as it ensures accurate and consistent color reproduction on physical materials where as RGB takes center stage in the digital space since it offers a wider range of vibrant colors to captivate your audience on screens. Now, go ahead and start embracing the power of color to enhance your brand identity and deliver a visually stunning experience across every touchpoint, i.e. from website to printed brochure.